OpenAI GPT-3 Model
by Stephen M. Walker II, Co-Founder / CEO
OpenAI GPT-3 Model
GPT-3, developed by OpenAI in 2020, was a landmark in the evolution of language models with its 175 billion parameters. As the third iteration in the GPT series, it significantly advanced the field of natural language processing.

GPT-3 excels in generating coherent, context-aware text, making it a versatile tool for applications ranging from content creation to advanced coding assistants.
Its introduction has not only pushed the envelope in machine learning research but also sparked important conversations about the ethical use of AI. The model's influence is profound, shaping perspectives on AI's societal roles and the future of human-machine collaboration.
History of GPT-3
GPT-3, or Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3, was released in 2020, following its 2019 predecessor, GPT-2. GPT-3 is a neural network machine learning model trained using internet data to generate any type of text.
At the time, it was the largest neural network ever built, with 175 billion machine learning parameters, which was 100 times larger than GPT-2.
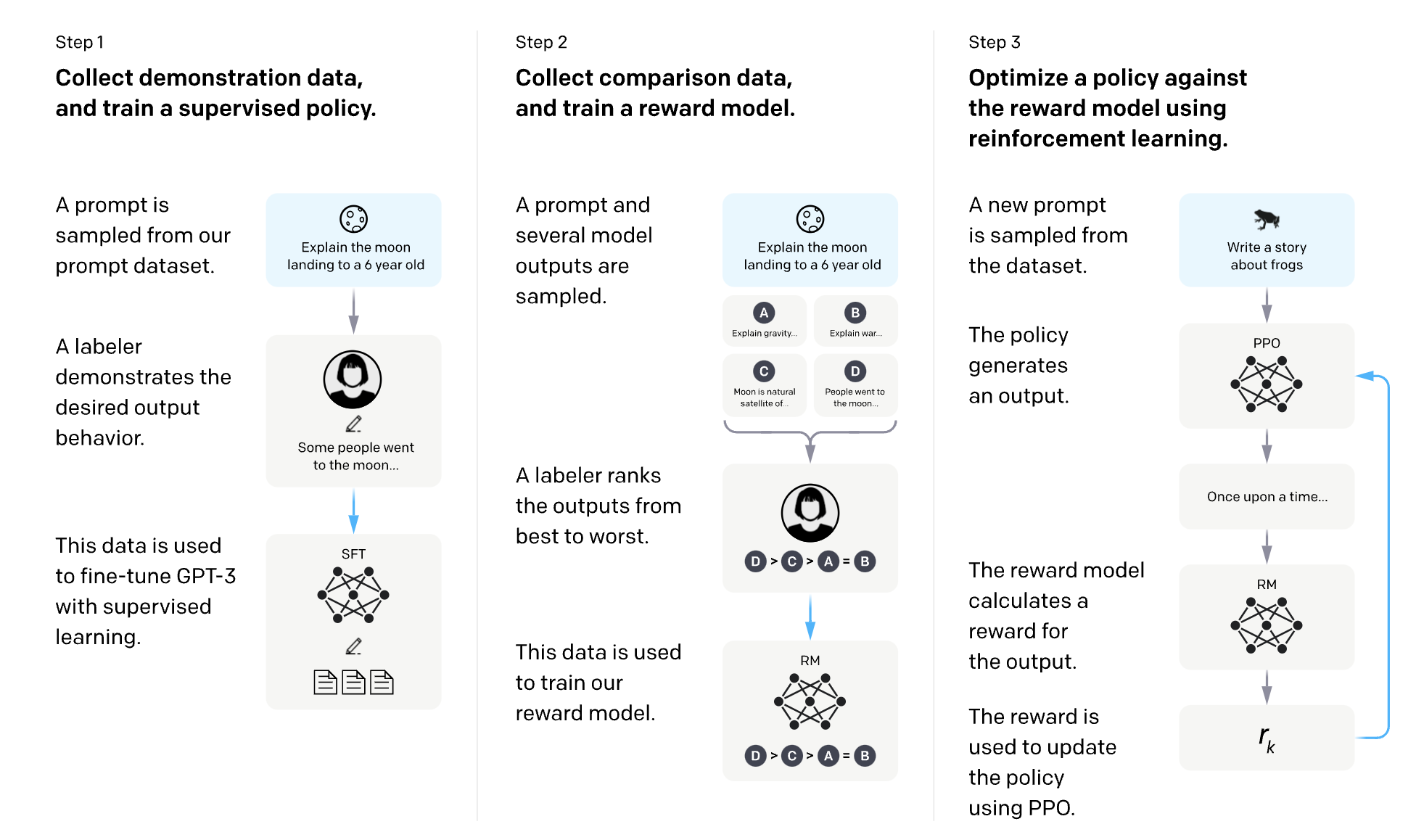
In 2019, OpenAI embarked on a series of research projects, one of which was the development of GPT-3. This model, a transformer-based deep-learning neural network, was trained on a vast corpus of text data, including books, articles, and web pages.
The training data was sourced from multiple datasets, including Common Crawl, webtexts, books, and Wikipedia, with the largest training set, CommonCrawl, constituting 45TB of compressed plaintext before filtering. GPT-3, with its 175 billion machine learning parameters, was a significant leap from its predecessor, GPT-2, and set a record as the largest neural network ever built.
The cost of training GPT-3 at the time was over $4.6 million when using a Tesla V100 cloud instance. This figure is supported by multiple sources, with estimates ranging from $500,000 to $4.6 million depending on the hardware used.
The training of GPT-3 was a resource-intensive process, utilizing 1 million GPU hours and necessitating an investment in GPUs valued at approximately $5 million. This investment underscores the computational demands of processing the model's 175 billion parameters and the breadth of data it was trained on.
It showed remarkable performance in various natural language processing tasks, including translation, question-answering, and cloze tasks, even surpassing state-of-the-art models.
One of the most powerful features of GPT-3 is its ability to perform new tasks by showing it a few examples of the task. For instance, it can translate sentences from one language to another after being shown a few examples of translated sentences. It was also able to generate "news articles" almost indistinguishable from human-made pieces.
GPT-3 has been used in various applications, such as natural language processing, text classification, and chatbots. It has been used in certain Microsoft products to translate conventional language into formal language, and in CodexDB to generate query-specific code for SQL processing. It was also used by The Guardian to write an article about AI being harmless to human beings.
The release of ChatGPT and GPT-3.5 Turbo, both based on the GPT-3 architecture, has been a significant development in the field of natural language processing. ChatGPT is a conversational AI model that can engage in human-like conversations with users.
Despite its impressive capabilities, GPT-3 has also raised concerns. GPT-2, the predecessor of GPT-3, was considered controversial as its creators deemed it too powerful and withheld its full version due to concerns that the model could be used to generate fake news and other forms of misleading information, potentially causing harm.
GPT-3 Variants
OpenAI released several variants of the GPT-3 model, each with different capabilities and use cases. The four main variants are Ada, Babbage, Curie, and Davinci, named after famous scientists and inventors.
-
Ada: The smallest variant with 350 million parameters. Capable of performing very simple tasks, it is the fastest and least costly model in the family.
-
Babbage: This variant has 1.3 billion parameters. It is capable of performing straightforward tasks, and it is very fast and lower cost.
-
Curie: This variant has 6.7 billion parameters. It is very capable, faster, and lower cost than Davinci. It is a good choice for tasks requiring a deeper understanding of context or more complex language generation.
-
Davinci: This is the largest and most capable GPT-3 model with 175 billion parameters. It can perform any task the other models can do, including code generation, often with higher quality.
There are also different versions of these models, such as text-davinci-003, which is part of the GPT-3 family and is designed to improve long-form content generation. Babbage-002 and Davinci-002 are replacements for the GPT-3 Ada and Babbage models, and GPT-3 Curie and Davinci models, respectively.
The GPT-3.5 Turbo model, despite being part of the GPT-3.5 series, is considered the most capable model of the GPT-3.5 family.
The specific model behind text-embedding-ada-002 is not publicly disclosed, but it uses elements from chat models 3.5 and 4.
GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct
GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct is a variant of the GPT-3.5 model developed by OpenAI. It is designed to excel in understanding and executing specific instructions, making it more adept at following instructions and reducing the generation of incorrect or harmful content.
This model diverges from its predecessor, GPT-3.5, in its core functionality. While GPT-3.5 was more focused on chat interactions, GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct is not designed to simulate conversations but is rather fine-tuned to excel in providing direct responses.
GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct is compatible with the legacy Completions endpoint and has similar capabilities as text-davinci-003. It is designed for instruction-following tasks and can handle a maximum of 4,097 tokens.
This model is a refined version of the GPT-3.5 series and was developed to improve user interaction with OpenAI's models. It was trained to address problems older models had, giving clearer and more on-point answers. This makes it a good fit for all kinds of uses, whether you know a lot about tech or not.
GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct is cost-effective and performs just as well as other GPT-3.5 models, making it a good choice for tasks that demand accuracy and clarity. It can be used for a variety of tasks, including generating different creative text formats, translating languages, answering questions in a comprehensive and informative way, and writing different kinds of creative content.
When to Use
GPT-3.5-Turbo-Instruct, developed by OpenAI, is tailored for specific instruction handling rather than chat interactions. It strikes a balance in performance and cost compared to other models in the GPT-3.5 series, offering a cost-effective solution for tasks requiring precise and efficient AI responses.
While generally competent for a range of tasks, GPT-3.5-Turbo-Instruct may not match GPT-4 or GPT-3.5-Turbo's proficiency in executing complex instructions. It is also not the optimal choice for conversational chat, which is the forte of models like ChatGPT, built specifically for such interactions.
For generating concise responses, GPT-3.5-Turbo-Instruct is preferable, whereas GPT-3.5-Turbo-16K is better for handling elaborate, conversational chat scenarios due to its higher token capacity.
Deprecation of GPT-3 Models
OpenAI announced the deprecation of older GPT-3 and GPT-3.5 models served via the completions endpoint on July 6, 2023. The deprecation process is part of OpenAI's strategy to continuously improve their models and services. The deprecation of GPT-3 and its variations using the Completions API is set to take place on January 4, 2024. Applications using the stable model names for base GPT-3 models (ada, babbage, curie, davinci) will automatically be upgraded to the new models listed above on this date.
Developers wishing to continue using their fine-tuned models beyond January 4, 2024, will need to fine-tune replacements atop the new base GPT-3 models (babbage-002, davinci-002), or newer models (gpt-3.5-turbo, gpt-4).
As for alternatives to GPT-3, there are several open-source options available. Some of these include Mixtral/Mistral 7b, Llama 2, and Phi2.
The latest breed of OpenAI models is the GPT-4 series, which are multimodal (they can take both text and image inputs), can solve much more complex problems thanks to advanced reasoning capabilities, and are typically much better at maths than previous models. However, GPT-4 models are significantly more expensive than GPT-3.5.
FAQs
What is GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct?
GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct is a variant of the GPT-3.5 model designed to follow specific instructions and generate direct responses. It is not intended for conversational chat but for tasks that require clear and concise AI-generated text.
When should I use GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct?
GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct is ideal for tasks that demand accuracy and clarity in the responses. It is cost-effective and performs well for generating creative text, translating languages, answering questions informatively, and writing various types of content.
What is the difference between GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct and other GPT-3 models?
GPT-3.5-turbo-instruct is fine-tuned for instruction-following tasks and is not designed for conversational purposes. It is a more refined version of the GPT-3.5 series, with improvements in providing clear and on-point answers.
What will happen to my application when GPT-3 models are deprecated?
Applications using the stable model names for base GPT-3 models will be automatically upgraded to the new models on the deprecation date. Developers wishing to continue using fine-tuned models will need to fine-tune replacements atop the new base models or newer models like gpt-3.5-turbo or gpt-4.
Are there any open-source alternatives to GPT-3?
Yes, there are several open-source options available, such as Mixtral/Mistral 7b, Llama 2, and Phi2. These can be considered as alternatives to GPT-3 for various applications.
openai gpt 3 just a few examples language models natural language generate computer code language model large language models previous models tens of thousands computer code gpt 3 internet data human dialogue api models english language task toxic language few shot learning training data fine tuning commercial product internet text updated model neural networks marketing teams machine learning parameter count input text text description news articles more data request access specific tasks openai announced several limitations limited number pre trained new features lower cost harmful applications allowing users greater accuracy models plain english small number model example developers system create examples users language ability generate user access code data new text tools future images technology focus languages version world large amounts team gpt 4 answers systems context api article tasks training openai api relevant services